Chronology of records
Study of the relative age of documents
Study of the relative age of documents
The study of the document’s relative age is based on indicating whether the analysed documents or their components (such as handwriting, signatures, prints, stamps, printed text) were made at the same time and the order of their application on the substructure of the document.
In expert practice, the subjects of document examination in such cases are the following issues:
- Study of overlapping records chronology.
- Examination of non-overlapping records (non-crossing) sequence.
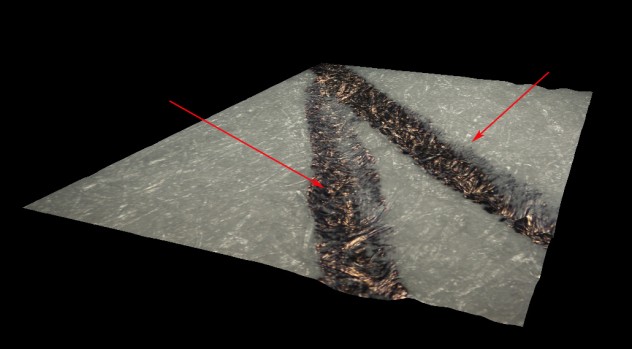

In the case of overlapping records, the following methods are currently used in criminology/forensics:
- Optical.
- Mechanical.
- Diffusion copying.
- Infrared luminescence.
- Computer (eg Photoshop, Scangraf).
- Electrostatic.
- Graphic-comparative.
- 3D technique.
- Spectroscopy (VSC, Raman).

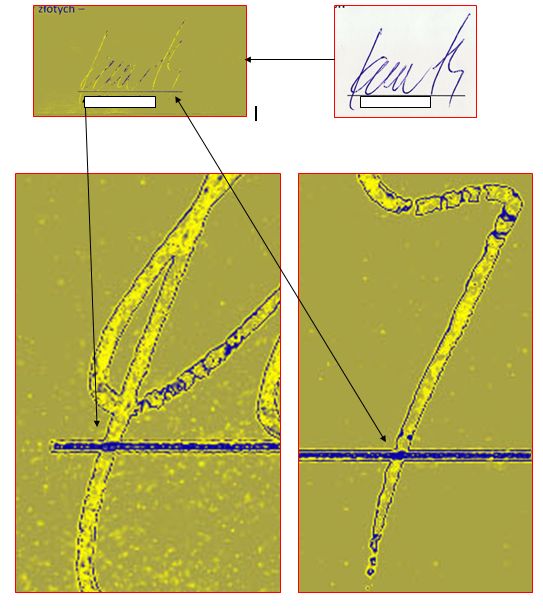
These issues have also become the subject of research experiments carried out within the development project at the University of Warsaw, the Research and Training Centre (now Criminalistics Institute) and Polish Forensic Association (development project No. OR 00001911, financed by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, finalized in 2012). The project’s premise was to develop an effective testing method for analysis of overlapping graphical lines on a paper substrate, made with different writing materials and printing techniques as well as non-overlapping graphical lines.
The research carried out within the project made it possible to work out more precise methods of indicating the chronology of records, using improved optical microscopy with 3D object tracking software as well as Raman microscopy.
